exe
execution stage
The goals of that stage are:
- Use the Imm/Registers to compute:
a. data to write back to register.
b. Calculate address for load/store
c. Calculate branch/jump target.
- Use the Imm/Registers to compute:
- Check branch condition.
- Data hazard detection and forwarding.
This stage is called Q102H.
instantiation of execution module in mini_core.sv
mini_core_exe mini_core_exe (
.Clock (Clock ), // input
.Rst (Rst ), // input
// Input Control Signals
.Ctrl (CtrlExe ), // input
.ReadyQ103H (ReadyQ103H ), // input
// Output Control Signals
.BranchCondMetQ102H (BranchCondMetQ102H ), // output
// Input Data path
//Q102H
.PreRegRdData1Q102H (RegRdData1Q102H ), // input
.PreRegRdData2Q102H (RegRdData2Q102H ), // input
.PcQ102H (PcQ102H ), // input
.ImmediateQ102H (ImmediateQ102H ), // input
//Q104H
.RegWrDataQ104H (RegWrDataQ104H ), // input
// output data path
.AluOutQ102H (AluOutQ102H ), // output
.AluOutQ103H (AluOutQ103H ), // output
.PcPlus4Q103H (PcPlus4Q103H ), // output
.DMemWrDataQ103H (DMemWrDataQ103H ) // output
);
Execution module mini_core_exe.sv
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Title :
// Project : mafia_asap
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// File :
// Original Author : Amichai Ben-David
// Code Owner :
// Adviser : Amichai Ben-David
// Created : 7/2023
//-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
`include "macros.sv"
module mini_core_exe
import common_pkg::*;
(
input logic Clock,
input logic Rst,
//===================
// Input Control Signals
//===================
input var t_ctrl_exe Ctrl,
input logic ReadyQ103H,
//===================
// Output Control Signals
//===================
output logic BranchCondMetQ102H ,
//===================
// Input Data path
//===================
//Q102H
input logic [31:0] PreRegRdData1Q102H,
input logic [31:0] PreRegRdData2Q102H,
input logic [31:0] PcQ102H,
input logic [31:0] ImmediateQ102H,
//Q104H
input logic [31:0] RegWrDataQ104H, // used for forwarding
//===================
// output data path
//===================
output logic [31:0] AluOutQ102H,
output logic [31:0] AluOutQ103H,
output logic [31:0] PcPlus4Q103H,
output logic [31:0] DMemWrDataQ103H
);
logic Hazard1Data1Q102H, Hazard2Data1Q102H, Hazard1Data2Q102H, Hazard2Data2Q102H;
logic [31:0] AluIn1Q102H, AluIn2Q102H;
logic [4:0] ShamtQ102H;
logic [31:0] RegRdData1Q102H, RegRdData2Q102H;
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// _____ __ __ _____ _ ______ ____ __ ___ ___ _ _
// / ____| \ \ / / / ____| | | | ____| / __ \ /_ | / _ \ |__ \ | | | |
// | | \ \_/ / | | | | | |__ | | | | | | | | | | ) | | |__| |
// | | \ / | | | | | __| | | | | | | | | | | / / | __ |
// | |____ | | | |____ | |____ | |____ | |__| | | | | |_| | / /_ | | | |
// \_____| |_| \_____| |______| |______| \___\_\ |_| \___/ |____| |_| |_|
//
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Execute
// -----------------
// 1. Use the Imm/Registers to compute:
// a) data to write back to register.
// b) Calculate address for load/store
// c) Calculate branch/jump target.
// 2. Check branch condition.
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Hazard Detection
assign Hazard1Data1Q102H = (Ctrl.RegSrc1Q102H == Ctrl.RegDstQ103H) && (Ctrl.RegWrEnQ103H) && (Ctrl.RegSrc1Q102H != 5'b0);
assign Hazard2Data1Q102H = (Ctrl.RegSrc1Q102H == Ctrl.RegDstQ104H) && (Ctrl.RegWrEnQ104H) && (Ctrl.RegSrc1Q102H != 5'b0);
assign Hazard1Data2Q102H = (Ctrl.RegSrc2Q102H == Ctrl.RegDstQ103H) && (Ctrl.RegWrEnQ103H) && (Ctrl.RegSrc2Q102H != 5'b0);
assign Hazard2Data2Q102H = (Ctrl.RegSrc2Q102H == Ctrl.RegDstQ104H) && (Ctrl.RegWrEnQ104H) && (Ctrl.RegSrc2Q102H != 5'b0);
// Forwarding unite
assign RegRdData1Q102H = Hazard1Data1Q102H ? AluOutQ103H : // Rd 102 After Wr 103
Hazard2Data1Q102H ? RegWrDataQ104H : // Rd 102 After Wr 104
PreRegRdData1Q102H; // Common Case - No Hazard
assign RegRdData2Q102H = Hazard1Data2Q102H ? AluOutQ103H : // Rd 102 After Wr 103
Hazard2Data2Q102H ? RegWrDataQ104H : // Rd 102 After Wr 104
PreRegRdData2Q102H; // Common Case - No Hazard
// End Take care to data hazard
assign AluIn1Q102H = Ctrl.SelAluPcQ102H ? PcQ102H : RegRdData1Q102H;
assign AluIn2Q102H = Ctrl.SelAluImmQ102H ? ImmediateQ102H : RegRdData2Q102H;
always_comb begin : alu_logic
ShamtQ102H = AluIn2Q102H[4:0];
unique casez (Ctrl.AluOpQ102H)
// Adder
ADD : AluOutQ102H = AluIn1Q102H + AluIn2Q102H; // ADD/LW/SW/AUIOC/JAL/JALR/BRANCH/
SUB : AluOutQ102H = AluIn1Q102H + (~AluIn2Q102H) + 1'b1; // SUB
SLT : AluOutQ102H = {31'b0, ($signed(AluIn1Q102H) < $signed(AluIn2Q102H))}; // SLT
SLTU : AluOutQ102H = {31'b0 , AluIn1Q102H < AluIn2Q102H}; // SLTU
// Shifter
SLL : AluOutQ102H = AluIn1Q102H << ShamtQ102H; // SLL
SRL : AluOutQ102H = AluIn1Q102H >> ShamtQ102H; // SRL
SRA : AluOutQ102H = $signed(AluIn1Q102H) >>> ShamtQ102H; // SRA
// Bit wise operations
XOR : AluOutQ102H = AluIn1Q102H ^ AluIn2Q102H; // XOR
OR : AluOutQ102H = AluIn1Q102H | AluIn2Q102H; // OR
AND : AluOutQ102H = AluIn1Q102H & AluIn2Q102H; // AND
default : AluOutQ102H = AluIn1Q102H + AluIn2Q102H;
endcase
if (Ctrl.LuiQ102H) AluOutQ102H = AluIn2Q102H; // LUI
end
always_comb begin : branch_comp
// Check branch condition
unique casez ({Ctrl.BranchOpQ102H})
BEQ : BranchCondMetQ102H = (RegRdData1Q102H == RegRdData2Q102H); // BEQ
BNE : BranchCondMetQ102H = !(RegRdData1Q102H == RegRdData2Q102H); // BNE
BLT : BranchCondMetQ102H = ($signed(RegRdData1Q102H) < $signed(RegRdData2Q102H)); // BLT
BGE : BranchCondMetQ102H = !($signed(RegRdData1Q102H) < $signed(RegRdData2Q102H)); // BGE
BLTU : BranchCondMetQ102H = (RegRdData1Q102H < RegRdData2Q102H); // BLTU
BGEU : BranchCondMetQ102H = !(RegRdData1Q102H < RegRdData2Q102H); // BGEU
default : BranchCondMetQ102H = 1'b0;
endcase
end
// Q102H to Q103H Flip Flops
`MAFIA_EN_DFF(DMemWrDataQ103H , RegRdData2Q102H , Clock, ReadyQ103H)
`MAFIA_EN_DFF(AluOutQ103H , AluOutQ102H , Clock, ReadyQ103H)
`MAFIA_EN_DFF(PcPlus4Q103H , (PcQ102H+32'd4) , Clock, ReadyQ103H)
endmodule
Code explanation - Data Hazard Detection Unit
// Hazard Detection
assign Hazard1Data1Q102H = (Ctrl.RegSrc1Q102H == Ctrl.RegDstQ103H) && (Ctrl.RegWrEnQ103H) && (Ctrl.RegSrc1Q102H != 5'b0);
assign Hazard2Data1Q102H = (Ctrl.RegSrc1Q102H == Ctrl.RegDstQ104H) && (Ctrl.RegWrEnQ104H) && (Ctrl.RegSrc1Q102H != 5'b0);
assign Hazard1Data2Q102H = (Ctrl.RegSrc2Q102H == Ctrl.RegDstQ103H) && (Ctrl.RegWrEnQ103H) && (Ctrl.RegSrc2Q102H != 5'b0);
assign Hazard2Data2Q102H = (Ctrl.RegSrc2Q102H == Ctrl.RegDstQ104H) && (Ctrl.RegWrEnQ104H) && (Ctrl.RegSrc2Q102H != 5'b0);
Lets take a look on some hazards that can occur in our pipeline:
add x1, x2, x3 # Q103H
add x4, x1, x5 # Q102H
In the second line we need x1 register value that is not ready yet because the instruction in Q103H is not finished yet.
add x1, x2, x3 # Q104H
add x4, x5, x6 # Q103H
add x7, x1, x8 # Q102H
In the third line we need x1 register value that is not ready yet because the instruction in Q104H is not finished yet.
another interesting examples:
add x1, x2, x3 # Q103H
sw x1, 0(x2) # Q102H
mini_core_exe abstract data hazard detection diagram
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------

---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Code explanation - Forwarding Unit
// Forwarding unite
assign RegRdData1Q102H = Hazard1Data1Q102H ? AluOutQ103H : // Rd 102 After Wr 103
Hazard2Data1Q102H ? RegWrDataQ104H : // Rd 102 After Wr 104
PreRegRdData1Q102H; // Common Case - No Hazard
assign RegRdData2Q102H = Hazard1Data2Q102H ? AluOutQ103H : // Rd 102 After Wr 103
Hazard2Data2Q102H ? RegWrDataQ104H : // Rd 102 After Wr 104
PreRegRdData2Q102H; // Common Case - No Hazard
// End Take care to data hazard
assign AluIn1Q102H = Ctrl.SelAluPcQ102H ? PcQ102H : RegRdData1Q102H;
assign AluIn2Q102H = Ctrl.SelAluImmQ102H ? ImmediateQ102H : RegRdData2Q102H;
RegRdData1Q102H - This is the data that is going to be used as the first operand in the ALU. We need to take care of data hazard. If the data is not ready yet, we need to forward it from the write back stage or from memory stage.
If Hazard1Data1Q102H equals to 1, it means that the register read data 1 (rs1) at decode stage (Q102H) is the same as the register write data (rd) at memory stage (Q103H) meaning that the read data is not ready yet. In this case, we forward data from Q103H stage directly to Q102H stage. The data calculated in the previous clock cycle and stored in AluOutQ103H.
If Hazard2Data1Q102H equals to 1, it means that the register read data 2 (rs2) at decode stage (Q102H) is the same as the register write data (rd) at write back stage (Q104H) meaning that the read data is not ready yet. In this case, we forward data from Q104H stage directly to Q102H stage.
In case when there is no hazard, we just take the data from the register file (PreRegRdData1Q102H).
AluIn1Q102H - This is the data that is going to be used as the first operand in the ALU. If SelAluPcQ102H equals to 1, it means that the ALU should use the PC as the first operand for instructions that adds immediate to Pc. If SelAluPcQ102H equals to 0, it means that the ALU should use the data from the register file as the first operand.
AluIn2Q102H - This is the data that is going to be used as the second operand in the ALU. If SelAluImmQ102H equals to 1, it means that the ALU should use the immediate as the second operand. If SelAluImmQ102H equals to 0, it means that the ALU should use the data from the register file as the second operand.
We assume that other parts of the code are relatively easy to understand. You may use the figure below to understand the flow of data in the execution stage.
mini_core_exe abstract execution diagram
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
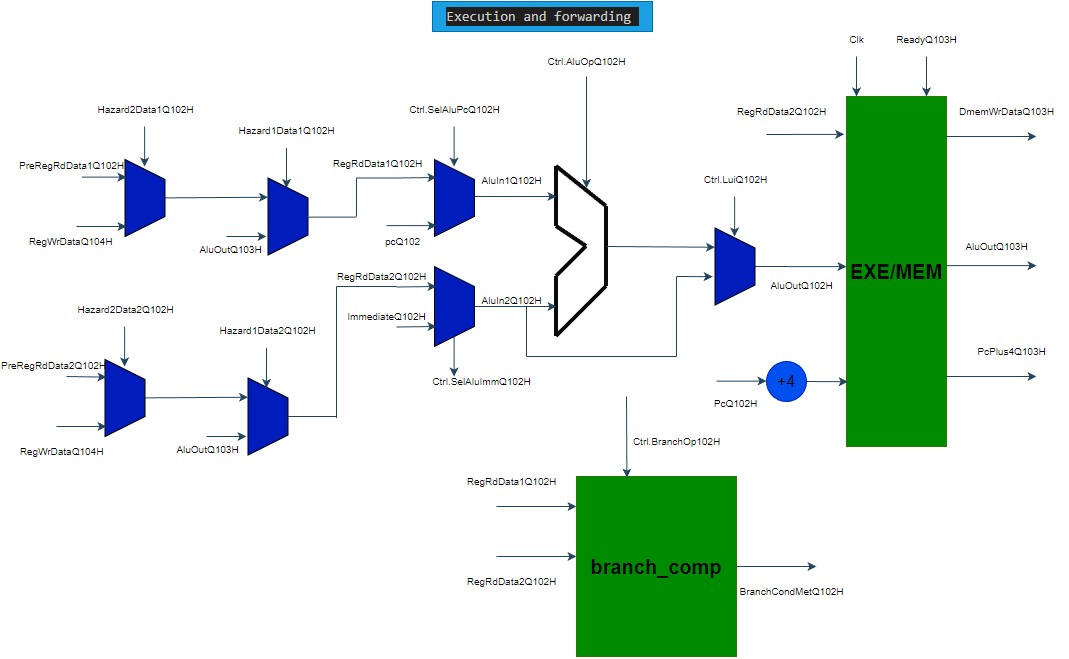 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Please note that the above implementation behaves correctly but the real hardware implementation can be changed depending on the synthesis tool you use.