mem_acs
memory access stage
- The goal of that stage is to access memory and get or store data in it.
- That stage is called Q103H
instantiation of mini_core_mem_access module in mini_core.sv
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// _____ __ __ _____ _ ______ ____ __ ___ ____ _ _
// / ____| \ \ / / / ____| | | | ____| / __ \ /_ | / _ \ |___ \ | | | |
// | | \ \_/ / | | | | | |__ | | | | | | | | | | __) | | |__| |
// | | \ / | | | | | __| | | | | | | | | | | |__ < | __ |
// | |____ | | | |____ | |____ | |____ | |__| | | | | |_| | ___) | | | | |
// \_____| |_| \_____| |______| |______| \___\_\ |_| \___/ |____/ |_| |_|
//
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Memory Access
// -----------------
// 1. Access D_MEM for Wrote (STORE) and Reads (LOAD)
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
mini_core_mem_acs mini_core_mem_access (
.Clock (Clock), //input
.Rst (Rst), //input
// Input Control Signals
.Ctrl (CtrlMem), //input
.ReadyQ104H (ReadyQ104H), //input
// Input Data path
.PcPlus4Q103H (PcPlus4Q103H), //input
.AluOutQ103H (AluOutQ103H), //input
.DMemWrDataQ103H (DMemWrDataQ103H),//input
// data path output
.Core2DmemReqQ103H (Core2DmemReqQ103H),//output
.PcPlus4Q104H (PcPlus4Q104H), //input
.AluOutQ104H (AluOutQ104H) //input
);
mini_core_mem_access.sv module
`include "macros.sv"
module mini_core_mem_acs
import common_pkg::*;
( input logic Clock, //input
input logic Rst, //input
// ctrl
input var t_ctrl_mem Ctrl, //input
input logic ReadyQ104H, //input
//data path input
input logic [31:0] PcPlus4Q103H,//input
input logic [31:0] AluOutQ103H, //input
input logic [31:0] DMemWrDataQ103H, //input
// data path output
output t_core2mem_req Core2DmemReqQ103H, //output
output logic [31:0] PcPlus4Q104H,//input
output logic [31:0] AluOutQ104H //input
);
// Outputs to memory
assign Core2DmemReqQ103H.WrData = DMemWrDataQ103H;
assign Core2DmemReqQ103H.Address = AluOutQ103H;
assign Core2DmemReqQ103H.WrEn = Ctrl.DMemWrEnQ103H;
assign Core2DmemReqQ103H.RdEn = Ctrl.DMemRdEnQ103H;
assign Core2DmemReqQ103H.ByteEn = Ctrl.DMemByteEnQ103H;
`MAFIA_EN_DFF(PcPlus4Q104H, PcPlus4Q103H, Clock, ReadyQ104H)
`MAFIA_EN_DFF(AluOutQ104H, AluOutQ103H , Clock, ReadyQ104H)
endmodule
Signal explanation
We communicate with the memory through the Core2DmemReqQ103H signal of
t_core2mem_reqtype. This signal is a structure that contains the following fields:WrData, Address, WeEn, RdEn, ByteEn.ByteEnallows us to choose the number of active bytes. For example, to distinguish between alborlhinstruction.The read information from the memory is returned to us through the
DMemRdRspQ104Hsignal threw the memory wrapper that will be discussed later.
mini_core_mem_acs general diagram
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
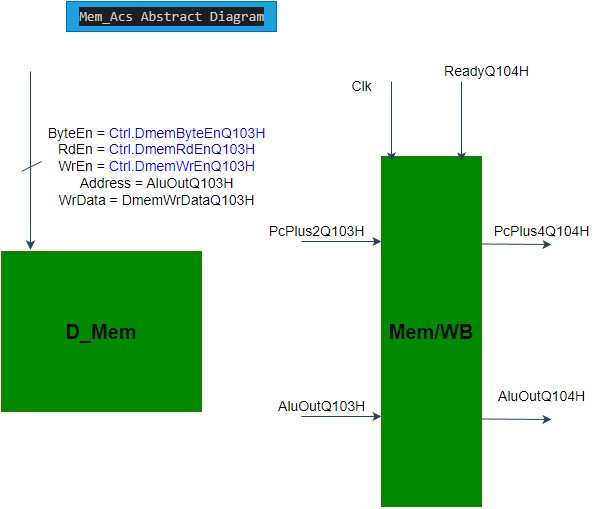
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------